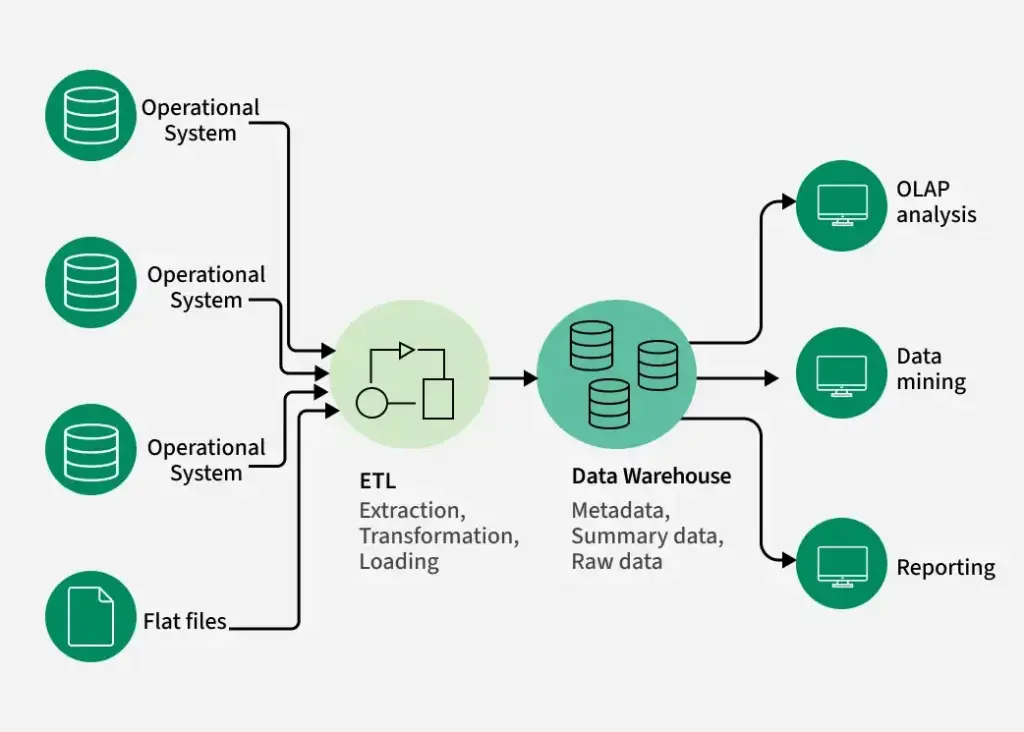
In today’s data-driven world, dashboards, machine learning models, and analytics reports all depend on one critical role: the Data Engineer.
While data scientists and analysts often get the spotlight, data engineers build the foundation that makes data usable, reliable, and scalable.
This blog explains what a data engineer actually does, the tools they use, and how data engineering works in real projects—in simple terms.
Who Is a Data Engineer?
A Data Engineer is responsible for designing, building, and maintaining systems that collect, process, and store data.
In short:
Data engineers make data ready for analysis.
They ensure that:
- Data is available on time
- Data is accurate and consistent
- Data systems can scale as data grows

What Does a Data Engineer Do Daily?
1. Build Data Pipelines
Data engineers create pipelines that move data from sources like:
- Databases
- APIs
- Logs
- Files (CSV, JSON, Parquet)
Example:
Moving sales data from a transactional database into a data warehouse every night.
2. Transform Raw Data
Raw data is often messy. Data engineers clean and transform it by:
- Removing duplicates
- Handling missing values
- Standardizing formats
Example:
Converting multiple date formats into a single standard format before reporting.
3. Manage Data Storage
They design and maintain:
- Data warehouses (Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift)
- Data lakes (S3, ADLS, GCS)
Goal: Store data efficiently and make it easy to query.
4. Ensure Data Quality & Reliability
Data engineers:
- Add validations and checks
- Monitor pipeline failures
- Fix broken data flows
Example:
Alerting the team if yesterday’s data load is missing or incomplete.
Common Tools Used by Data Engineers
| Category | Tools |
|---|---|
| Programming | Python, SQL |
| Data Processing | Spark, Pandas |
| Orchestration | Airflow, Prefect |
| Warehouses | Snowflake, BigQuery |
| Cloud | AWS, Azure, GCP |
| Version Control | Git |